Green tea polyphenols in tea can fight free radicals off the hook and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, making them the "natural preservative" of the beauty industry!
Just how powerful are they?

◆ What are Green Tea Polyphenols?
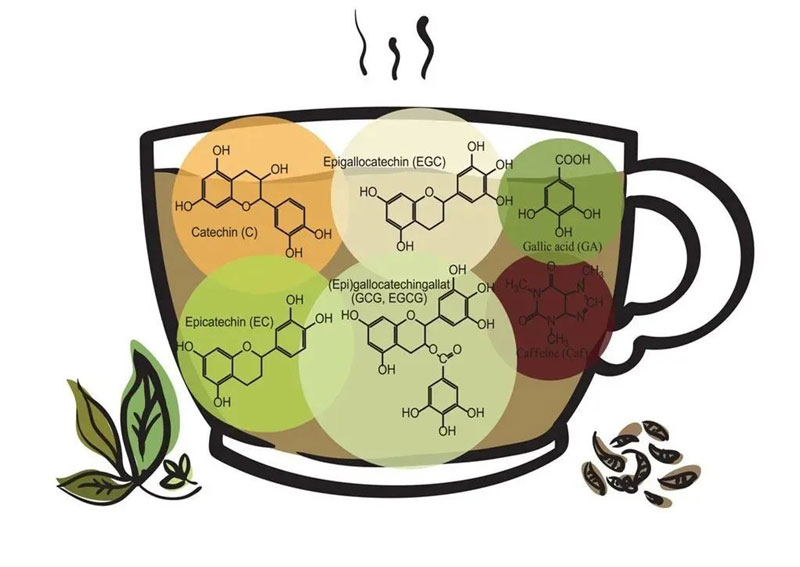
Green Tea Polyphenols, or GTP for short, are the primary compounds found in tea leaves, accounting for 18%-36% of the total dry matter content.
GTP isn't actually a single compound, but rather a general term for polyphenols in tea. Based on their chemical structure, they can be divided into four categories:
- Catechins (flavanols)
- Flavonoids (anthocyanidins)
- Phenolic and dextran acids
- Anthocyanidins
Catechins are the most abundant, accounting for approximately 75% of the total GTP content.
GTP is one of the primary components that contribute to tea's color, aroma, and flavor, and also has important health implications for human physiology.
◆ GTP's Effects
GTP has strong antioxidant activity, effectively reducing free radical levels and inhibiting lipid peroxidation.
Research has shown that 1 mg of GTP is as effective as 9 micrograms of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in scavenging harmful excess free radicals, significantly exceeding the activity of other similar substances. GTP's antioxidant activity is 18 times stronger than vitamin E and has a synergistic effect with vitamins C and E.
01. Anti-Cancer
Popular studies have shown that consuming tea (at least 250 mg of catechins daily) can reduce the risk of cancer. GTP can block the synthesis of various carcinogens in the body, such as nitrite, and has the potential to directly kill cancer cells, activate tumor cell-suppressing signaling pathways, and enhance the body's immune system.
Of course, this doesn't mean that drinking tea can completely eliminate cancer, but as a supplemental health strategy, its value is self-evident.
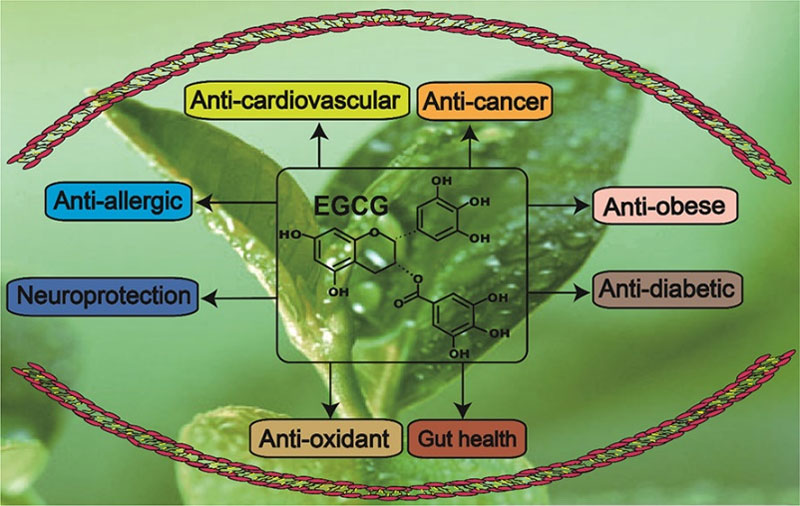
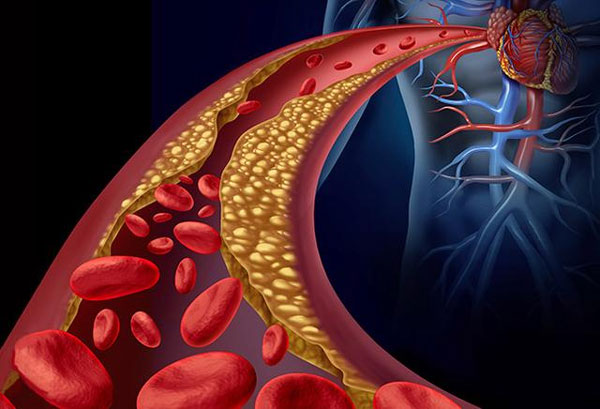
02. Cardiovascular Protection
GTP is highly effective in preventing and improving cardiovascular disease. On the one hand, it inhibits the oxidation of cholesterol and unsaturated fatty acids, reducing their deposition on arterial walls, keeping blood vessels clean and unobstructed, and preventing atherosclerosis.
On the other hand, the catechins ECG and EGC in GTP, as well as their oxidation products, theaflavins, can reduce fibrinogen levels, promote clearer blood coagulation, inhibit thrombosis, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
03. Other Benefits
In addition to the primary biological activities mentioned above, GTP also possesses a variety of other pharmacological effects that benefit health.
For example, it offers radiation protection, being known as a natural UV filter. In terms of skin protection and treatment, GTP can effectively prevent UV damage to the skin, offering anti-aging, anti-wrinkle, and anti-allergy benefits.
Furthermore, GTP's natural deodorizing properties have led to its widespread use in products such as chewing gum and oral sprays, effectively removing food and breath odors.

◆ Conclusion
While GTP possesses numerous benefits, tea is not a medicine and cannot directly replace medication. For related conditions, medication should still be taken as directed by a doctor. In daily life, drinking tea regularly offers numerous health benefits. A healthy lifestyle begins with a cup of tea.

%20--%3e%3c!DOCTYPE%20svg%20PUBLIC%20'-//W3C//DTD%20SVG%201.1//EN'%20'http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd'%3e%3csvg%20version='1.1'%20id='图层_1'%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20xmlns:xlink='http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink'%20x='0px'%20y='0px'%20width='256px'%20height='256px'%20viewBox='0%200%20256%20256'%20enable-background='new%200%200%20256%20256'%20xml:space='preserve'%3e%3cpath%20fill='%23FFFFFF'%20d='M194.597,24.009h35.292l-77.094,88.082l90.697,119.881h-71.021l-55.607-72.668L53.229,232.01H17.92%20l82.469-94.227L13.349,24.009h72.813l50.286,66.45l58.148-66.469V24.009z%20M182.217,210.889h19.566L75.538,44.014H54.583%20L182.217,210.889z'/%3e%3c/svg%3e)




