The thyroid gland is the largest endocrine organ in the human body. The thyroid hormones it secretes play an important role in the growth, development, metabolism and other physiological processes of the human body.
With the increasing incidence of thyroid diseases, it poses a considerable threat to people's health.
If you unfortunately suffer from thyroid disease, you must learn to eat properly. A reasonable diet not only helps to control the disease, but also helps to improve symptoms and improve the quality of life.
Different types of thyroid diseases have their own dietary taboos. Here are some dietary suggestions for different thyroid diseases!
◆ Dietary principles
Supplementation of energy, protein and vitamins
1. Hyperthyroidism
When suffering from hyperthyroidism, the body is like a machine running at an overspeed, the metabolic rate increases, and energy consumption increases. Therefore, it is crucial to follow the dietary principle of "three highs and one limit", that is, high energy, high protein, high vitamins, and at the same time limit iodine intake.
Choose carbohydrate-rich foods, such as rice, noodles, bread, potatoes, etc., to ensure that the body has enough energy to support daily activities and metabolic needs.
Sources of high-quality protein include: beef, pork, chicken, fish, shrimp, eggs, dairy products, beans, etc. These proteins help maintain muscle mass, promote tissue repair and maintain the normal function of the immune system.
High vitamin intake is also essential for patients with hyperthyroidism. Fresh vegetables and fruits are important sources of vitamins, such as spinach, broccoli, carrots, oranges, kiwis, strawberries, etc., which are rich in antioxidant vitamins such as vitamin A, C, and E, which help reduce the damage of oxidative stress to the body.
At the same time, iodine intake should be strictly limited, and iodine-rich seafood such as kelp, seaweed, marine fish, and shrimp should be avoided. Use iodine-free salt when cooking.
2. Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism patients have a relatively low metabolic rate and reduced energy requirements, but they still need to ensure adequate nutrient supply.
Increasing protein intake in moderation helps maintain the body's normal physiological functions, such as lean meat, fish, beans, eggs and other foods rich in high-quality protein.
Although there is no clear evidence that patients with hypothyroidism have special changes in their iodine needs, it is generally recommended to consume iodine-containing foods in moderation, such as kelp and laver, to maintain normal thyroid function.
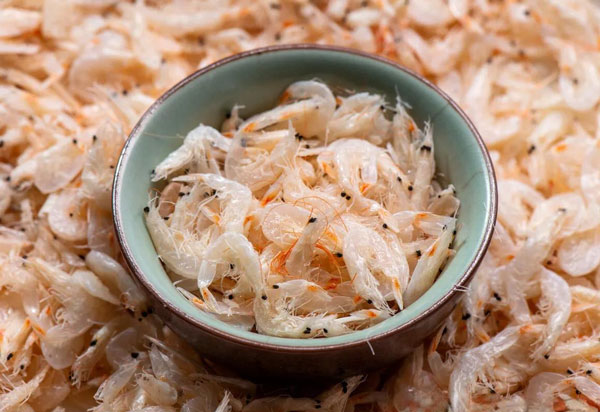

◆ Iodine intake
1. Hyperthyroidism
For patients with hyperthyroidism, excessive iodine will further stimulate the synthesis and release of thyroid hormones and aggravate the condition. Therefore, high-iodine foods should be strictly avoided, such as various seaweeds (kelp, laver, wakame), shellfish (mussels, scallops, oysters), marine fish (cod, salmon, tuna), etc.
In addition to iodine in food, it is also necessary to avoid the use of iodine-containing drugs and cosmetics, such as iodine-containing contrast agents, iodine tincture, etc.
2. Hypothyroidism
For hypothyroidism caused by iodine deficiency, appropriately increasing iodine intake can help improve thyroid function. Iodine-containing foods can be consumed in moderation.
However, for hypothyroidism caused by Hashimoto's thyroiditis, excessive iodine intake may aggravate the autoimmune response of the thyroid gland. Therefore, iodine intake should be moderate and not excessive.
◆ Food selection
1. Recommended food
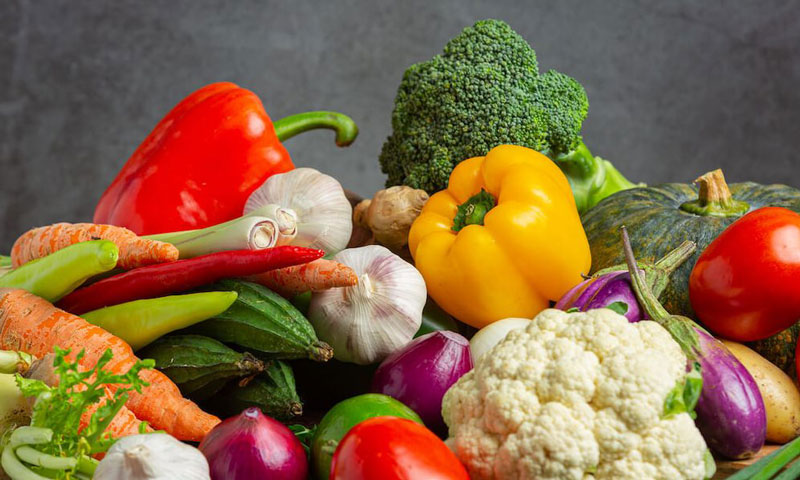
1) Fresh fruits and vegetables
Fresh vegetables and fruits are not only rich in vitamins and minerals, but also rich in dietary fiber and antioxidants.
- Green vegetables such as spinach, broccoli, celery, etc. help maintain cardiovascular health and normal intestinal function.
- Orange and red vegetables, such as carrots, pumpkins, tomatoes, etc., are rich in carotene and vitamin C, and have antioxidant and immune-enhancing effects.
- For the choice of fruits, apples, bananas, oranges, strawberries, blueberries, etc. are all good choices. They have natural sugars, vitamins and minerals.

2) Animal food
Fish, chicken, duck, etc. are good sources of high-quality protein and unsaturated fatty acids.
Chicken and duck are rich in protein and relatively low in fat, suitable as daily protein supplements.
3) Coarse grains and beans
Coarse grains and beans such as soybeans and brown rice are rich in dietary fiber, B vitamins and minerals, which help regulate blood sugar and blood lipid levels, promote intestinal peristalsis, and prevent constipation.
B vitamins play an important role in energy metabolism and nervous system function.
2. Foods not recommended
1) Stimulating beverages
Caffeine in coffee and tea may stimulate the nervous system, causing symptoms such as increased heart rate and insomnia, and aggravating the symptoms of hyperthyroid patients. Alcohol can burden the liver, affect the body's metabolic function, and is not conducive to the recovery of thyroid disease.
2) Greasy and spicy foods
Fried foods contain a lot of oil, which can easily lead to increased blood lipids and increase the cardiovascular burden. Spicy foods such as chili and pepper may irritate the gastrointestinal tract and cause discomfort.
3) Processed foods and high-salt foods
Processed foods such as canned foods usually contain a lot of additives, sugar and salt, and have low nutritional value. High-salt foods such as pickles can cause water and sodium retention, aggravating edema and hypertension.
◆ Emotional factors
1. The impact of emotions on the thyroid gland
Long-term negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and anger may interfere with the normal function of the thyroid gland by affecting the neuroendocrine system.
Excessive stress may affect the synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones.
2. Psychological adjustment and diet
Maintaining a good mental state is essential for the recovery of thyroid disease. Psychological counseling through exercise, listening to music, etc. can reduce stress and improve mood.
Some foods that have a calming effect on the mind, such as lily, red dates, etc., can also be appropriately added to the daily diet.
◆ Other precautions
1. Use drugs with caution
Certain foods may affect the absorption and metabolism of thyroid drugs. For example, isoflavones contained in soybeans and their products may interfere with the absorption of thyroid hormones.
To ensure the efficacy of the drug, it is recommended to take thyroid drugs on an empty stomach, generally 30-60 minutes before breakfast.
2. Lifestyle habits
Avoid overwork and give the body enough rest time, which is conducive to restoring physical strength and regulating endocrine function. Ensure adequate sleep.
Adequate exercise helps to strengthen physical fitness, improve immunity, and improve mood. Choose a suitable exercise method, such as walking, jogging, etc., combining work and rest, and moderate.
The dietary precautions for patients with thyroid disease need to be adjusted individually according to their specific condition, and everything should be subject to the doctor's advice.

%20--%3e%3c!DOCTYPE%20svg%20PUBLIC%20'-//W3C//DTD%20SVG%201.1//EN'%20'http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd'%3e%3csvg%20version='1.1'%20id='图层_1'%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20xmlns:xlink='http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink'%20x='0px'%20y='0px'%20width='256px'%20height='256px'%20viewBox='0%200%20256%20256'%20enable-background='new%200%200%20256%20256'%20xml:space='preserve'%3e%3cpath%20fill='%23FFFFFF'%20d='M194.597,24.009h35.292l-77.094,88.082l90.697,119.881h-71.021l-55.607-72.668L53.229,232.01H17.92%20l82.469-94.227L13.349,24.009h72.813l50.286,66.45l58.148-66.469V24.009z%20M182.217,210.889h19.566L75.538,44.014H54.583%20L182.217,210.889z'/%3e%3c/svg%3e)